The Bogoliuby Medical Center provides a wide range of diagnostic and treatment procedures, including prostate biopsy.
A prostate biopsy - is a diagnostic test designed to take small samples of prostate tissue, which are subsequently examined microscopically to confirm or except cancer.
When it is necessary?
Common indications for prostate biopsy are: an increase in blood values of a specific prostate antigen ((PSA); suspicious conditions detected during transrectal ultrasound; detection of abnormal formations during rectal examination); suspicious conditions detected during transrectal ultrasound; transrectal ultrasound; detection of abnormal formations during rectal examination.
detection of abnormal formations during rectal examination. In the presence of any abnormalities, a biopsy is performed specifically to confirm or refute clinical data. Statistics show that of the four men who are tested for moderately high PSA levels (4–10 ng / ml), only one person has prostate cancer. Fortunately, many prostate formations are benign or develop slowly without causing significant problems. However, there are cases when the disease develops rapidly and forms metastases already at an early stage.
Prostate cancer is very rare in men under the age of forty-five, but starting at this age, it is important to be checked regularly, especially if there is difficulty urinating, burning and pain when urinating, hematuria or a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
How’s biopsy going?
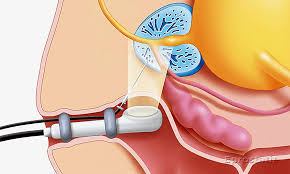
During a biopsy, the patient lies on his side, first a prophylactic ultrasound examination of the rectum and prostate is performed. Thus, the absence of contraindications is established. Next, a small dose of anesthetic is injected through the probe. Because of this, a prostate biopsy is a painless and usually well-tolerated test.
Using a special biopsy needle, the doctor takes several fragments of the prostate gland. An ultrasound probe helps the urologist to monitor the process of taking the material.
Microscopic analysis of tissue samples makes it possible to distinguish between healthy and cancerous cells and, ultimately, to determine their location and degree of abnormality. For this purpose, the Gleason score is used. A score of one to five indicates a small abnormality, above five - a high degree of abnormality, with a high probability that the tumor develops and spreads rapidly. In the case of pathological, but not necessarily cancerous results, a second biopsy is usually required after three to six months to establish the absence of ongoing tumor processes.
Are complications possible?
Anyway, a prostate biopsy is an invasive diagnostic procedure and, therefore, is burdened with a number of risks associated with the type of anesthesia, the patient's age and his general condition.
In particular, the intervention can lead to hemorrhagic, inflammatory, infectious complications. Hemorrhagic complications are the most common, occurring in 20% of cases. Usually this is mild and transient bleeding, as evidenced by traces of blood in the urine, ejaculate or feces.
Within certain limits, this is a normal phenomenon that can last for several days. Inflammatory complications cause swelling of the gland, which interferes with normal urinary outflow. They are rare (less than 1% of cases), but a catheter may be required.
In the presence of infectious complications (cystitis, infectious prostatitis epididymitis) difficulty urinating is associated with fever. In this case, antibiotics come to the rescue, the use of which is advisable for several days after the end of the biopsy. Many of these complications can be prevented, or at least reduced, by carefully following the doctor’s instructions regarding preparation for the test.
How to prepare?
To prevent serious bleeding episodes, it is important to stop taking biopsy drugs that reduce blood coagulation (warfirin, ibuprofen, etc.), as well as herbal supplements that have similar properties (ginkgo biloba, ginger, garlic). The doctor prescribes an antibiotic per day to prevent the risk of infection. And twelve hours before the procedure, a cleansing enema should be done. On the day of the biopsy, you should not eat, it is carried out on an empty stomach.