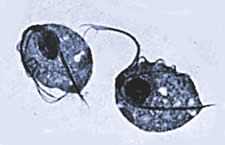
Vaginal trichomonas - trichomonas is the name of flagellate protozoa typical of the female reproductive tract and responsible for one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases in the world - trichomoniasis.
Trichomonas does not penetrate into the tissues, but carries out its pathogenic activity in epithelial cells. This parasite has the ability to attach its flagella to the walls of the vagina. Trichomonas increases the vaginal pH, destroying the "good" lactobacilli, which protect the body from infection. Trichomonas, the reduced natural acidity of this delicate area of the female body, make it easy for other infectious agents to invade it.
The disease is almost always sexually transmitted, but in recent years there has been a significant increase in the transmission of Trichomonas by the household, through normal contact with hygiene items - a towel, linen.
Trichomoniasis is widespread on all continents and in all climatic zones. The incidence is about 170 million cases per year, and, like many other STDs, , the disease can contribute to HIV transmission (causing local accumulation of macrophages and lymphocytes).
Human being is the only natural host of Trichomonas. In the external environment, the vaginal trichomonas does not live long - up to 30 minutes in warm water. The disease is characteristic of fertile age and very rarely affects before menstruation or after menopause.
Symptoms of trichomoniasis
Symptoms such as:
- severe itching;
- foamy, yellowish discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- painful urination may indicate a possible infection with trichomoniasis.
Variability of symptoms is observed in various phases of the menstrual cycle. In men, in most cases, the infection is asymptomatic.
Diagnosis of trichomoniasis
An accurate diagnosis is made in the laboratory after examination of vaginal smears in women or urethral exudate and sperm in men.
Trichomoniasis Treatment
If timely treatment is not carried out, trichomoniasis develops from acute to chronic relapsing disease.
To prevent trichomoniasis, avoid accidental sexual intercourse, pay attention to towels in hotels.
The drugs are most active in the fight against Trichomonas infection - this is a group of nitroimidazoles. It is important that the patient’s partners also receive antibiotic therapy, regardless of whether they have clinical symptoms of the disease or not. Until the end of drug therapy should refrain from sexual intercourse.