The polyps are dangerous and how to get rid of them, says the obstetrician-gynecologist, reproductologist, gynecologist-endocrinologist, doctor of the highest category of Bogoliuby MC Evgenia Schepko.
What are polyps, what are they and where do they come from?
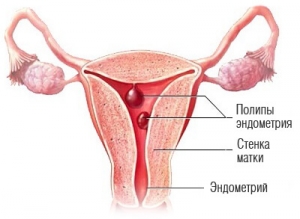
The endometrial polyp - is a small growth on the inner lining of the uterus, which is attached to it by the leg. Polyps are formed as a result of an increased level of estrogen in the body and excessive growth of the endometrium in one place. The dimensions of the polyp can range from 2-3 millimeters to several centimeters. Sometimes they can even be seen in the vagina during a gynecological examination on a chair. Most often, such long polyps are found in older women.
Large polyps are sometimes confused with small submucous myomas. It is important to differentiate them, because it is necessary for the further selection of treatment methods.
By structure, polyps are glandular (characteristic of young women), fibrous (usually diagnosed in older women), glandular-fibrous, less commonly adenomatous (especially dangerous, because they can change and become malignant).
The formation of polyps is facilitated by hormonal disorders, overweight, malfunctioning of the thyroid gland, diabetes mellitus, stress.
Who is more likely to be diagnosed with polyps?
If earlier polyps were diagnosed in women after 35 years, now adenomatous polyps (precancerous endometrium) occur even in 25-year-olds. That is, we can say that the disease is significantly younger.
Why are polyps dangerous?
Polyps are dangerous in that they tend to degenerate into malignant, oncological. One of the 100 identified polyps has atypical cells. In this case, we are talking about endometrial cancer.
Why do polyps degenerate into malignant?
This is influenced by many factors. The key role is played by the activity of the human papillomavirus and a genetic predisposition to cancer. For example, if someone's family has cancer patients, then even a healthy person is at risk. In addition, if he is a carrier of human papillomavirus, especially its oncogenic types, he should be especially attentive to his health.
So, women belonging to risk groups, after detecting polyps, need to remove them as soon as possible. In this case, monitoring the course of the disease does not make sense: the polyp, regardless of its size, must be removed.
What are the symptoms of this disease?
With polyps, a slight malfunction of the menstrual cycle is possible: : before or after menstruation, there may be slight spotting, not even red, but pale brown. Abundant menstruation, infertility, unsuccessful attempts at artificial insemination are also possible. One of the symptoms is the appearance of spotting in women during menopause.
How are polyps diagnosed?
If the polyp leaves the uterine cavity and is contained in the cervix or vagina, the doctor can see it on a gynecological chair. But this does not always happen.
You can diagnose polyps during transvaginal ultrasound. The best period for the diagnosis of the endometrial polyp (then it is better visualized) is from 4 to 7 days of the menstrual cycle. An ultrasound diagnosis on the right days of the menstrual cycle is enough to make a diagnosis.
How to treat endometrial polyps?
The ideal way - hysteroscopy - cutting, die cutting polyp.
Sometimes women get rid of polyps by curettage. But this is not the treatment that I would recommend. The fact is that curettage occurs blindly, and therefore there is no guarantee that the polyp will be completely removed. A leg may remain in the uterine cavity, and the polyp will grow again, but this time much faster. Therefore, I do not advise doing curettage: this is not a treatment method for endometrial polyps. You can resort to curettage to stop bleeding, but no more.
Hysteroscopy is just the beginning of treatment. After this procedure, hormone therapy is prescribed, which is designed to regulate the hormonal background.
Treatment with drugs, most often oral contraceptives, lasts at least another three months. If a woman has an adenomatous or other polyp with atypical cells, she is referred to an oncogynecologist who prescribes further treatment. If the atypia goes beyond the polyp, this is a show until the uterus is completely removed.
Another method for treating polyps is endometrial ablation. It occurs like a hysteroscopy, but with this method, the vessels of the organ are closed. As a rule, this treatment is recommended for older women who do not plan to give birth anymore. This procedure is quite traumatic for the endometrium, but it is guaranteed to prevent the re-emergence of polyps. And they, as a rule, very often reappear.
If you remove the polyp and incorrectly prescribe hormone therapy, that is, do not eliminate the main factor in the occurrence of polyps, they will appear again.
Can a woman with endometrial polyps get pregnant?
With polyps of small size and depending on their location, pregnancy is possible. But there is also a threat of abortion. The main thing is to maintain pregnancy until the laying and formation of the placenta, then polyps do not pose a risk to pregnancy, because they do not grow.
Can polyps after birth appear again?
After pregnancy, polyps usually disappear. After all, the best treatment for any myomas and polyps is to stop their blood supply, nutrition. This occurs, for example, with menopause: artificial (drug) or natural (due to a certain age) or pregnancy.
What do you advise women to do to prevent the appearance of polyps?
It is necessary to abandon abortions, refrain from surgical interventions and any trauma to the endometrium, and try to get pregnant for the first time before the age of 30. And be sure to at least once a year undergo a full examination by a gynecologist. Do not self-medicate, do not arbitrarily take without a doctor's prescription. Monitor your health, thyroid function, timely eliminate endocrine disorders, eat a balanced diet.