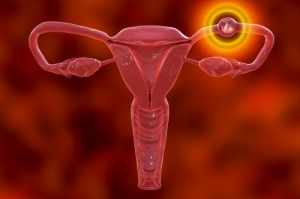
The diagnosis of an ectopic pregnancy usually takes the patient by surprise and often represents a real psychological trauma. Ectopic pregnancy accounts for 1% to 2% of conceptions. A slightly higher probability (about 4%) is observed in the case of assisted fertilization procedures.
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
The term ectopic indicates that the embryo implants outside the uterus. In a normal conception, a sperm fertilizes an egg inside the tube, and the fertilized egg travels down the tube and reaches the uterus within 6 to 10 days. If this does not happen and the embryo implants in the wall of the tube, the tube cannot support the growth of the embryo and within a few weeks it ruptures, resulting in potentially fatal bleeding if not treated promptly and adequately.
More than 90% of ectopic pregnancies occur in the tubes, but the embryo can also implant in the cervix, ovaries, or inside the abdominal cavity. Abdominal pregnancies are extremely rare and are often diagnosed only in the later stages.
Why does ectopic pregnancy occur?
In most cases, the reason for implantation in the wrong anatomical location is unclear, but very often it is due to pre-existing problems with the fallopian tubes (the estimated percentage is between 30 and 50% of cases). In fact, any event that affects the patency of the tubes can increase the risk of implantation in the tubes. These include: taking certain medications, abdominal surgery, endometriosis , sexually transmitted diseases, intrauterine device (IUD).
What are the signs of an ectopic pregnancy?
Symptoms usually appear between the fourth and twelfth weeks and may include: abdominal pain, more intense on one side; vaginal bleeding; discomfort and pain when urinating and defecating; shoulder pain. Note that a pregnancy test is positive even in the case of an ectopic pregnancy.
Vaginal bleeding is usually different from normal menstruation. It tends to appear in alternating phases, first a watery discharge, then a dark brown discharge . In some cases, when a woman is unaware that she is pregnant, it may be mistaken for abnormal menstrual flow and therefore delay diagnosis, worsening the prognosis.
Fortunately, most ectopic pregnancies are now diagnosed early, often before the patient even begins to experience symptoms that could lead to irreversible complications. Hormonal tests ( beta-hCG ) and ultrasound have significantly improved diagnostic capabilities.
What is the danger of an ectopic pregnancy?
If an ectopic pregnancy is recognized early, the prognosis for the mother is good. Future fertility depends on several factors, the most important of which is the history of infertility. Ectopic pregnancies are often due to pre-existing tubal abnormalities, and for this reason there is an increased risk of subsequent ectopic pregnancies.
Loss of a tube will significantly affect fertility. In such cases, it makes sense to resort to assisted reproduction methods to get around this problem. Specialists at the Bogolyuby Medical Center often recommend waiting three to six months after therapy before trying to get pregnant again. From a statistical point of view, it is worth noting that for women with previous full-term pregnancies, the probability of a new physiological pregnancy is 80%. For nulliparous patients (without previous pregnancies), the probability is slightly lower (about 50%).
Many women diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy, especially if they have been trying for a long time to have a baby, wonder whether it is possible to transfer an embryo from the tube to the uterus. Unfortunately, such an intervention is currently not possible.